Formula Errors in Excel
This chapter helps you understand and correct typical formula errors in Excel. Let’s start simple.
#####
If you see this error code, it means the column needs to be wider to display the cell’s content.

1. Click and drag the right border of the header for column A to resize it.
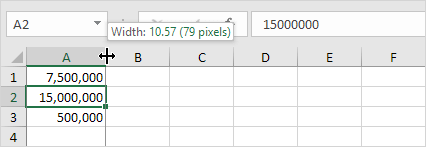
Tip: Double-click the right side edge of column A to make it fit the longest content.
#NAME?
The #NAME? error happens when Excel fails to recognize text within a formula.
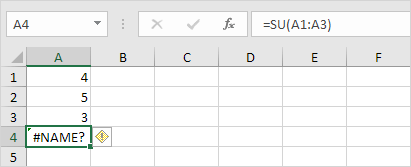
1. Simply correct SU to SUM.
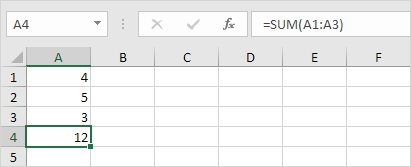
#VALUE!
You see the #VALUE! Error in Excel when a formula has an argument that Excel doesn’t understand or expects a different type.

1a. Replace the content of cell A3 with a numerical value.
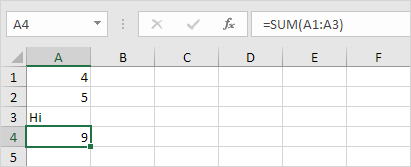
1b. Use a function that ignores cells if they have text.
#DIV/0!
When an Excel formula attempts to divide a number by zero or an empty cell, it shows the error #DIV/0!
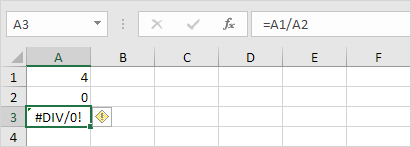
1a. Replace the value in cell A2 with any number except 0.
1b. Avoid displaying the error by using the IF function.
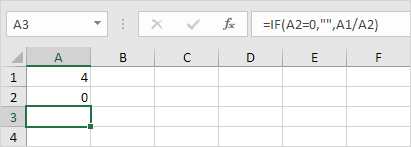
Explanation: When cell A2 is 0, an empty string (“”) will appear in the cell. Otherwise, the formula will show the result of A1 divided by A2.
#REF!
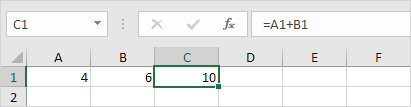
When a Excel formula refers to a cell that does not exist, the #REF! Error occurs.
1. Cell C1 refers to cells A1 and B1, meaning it uses their contents to produce its own value.
2. Delete column B. To remove it, right-click on the column B header and then click Delete.
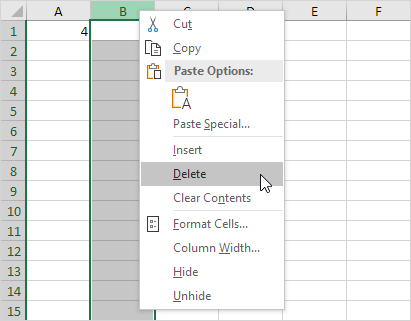
3. Select cell B1. The reference to cell B1 is not recognized anymore.
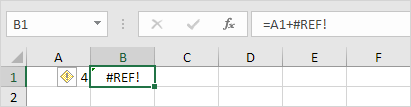
4. To fix this error, select cell B1 and from the formula bar delete “+#REF!”, or undo your last step (use CTRL + Z).
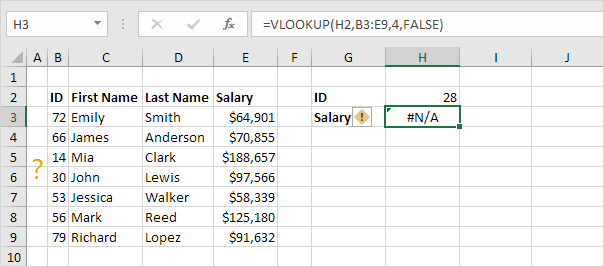
#N/A
When VLOOKUP or related functions such as XLOOKUP and MATCH fail to find a match, they return the #N/A error.
1. In the example below, ID 28 is missing.
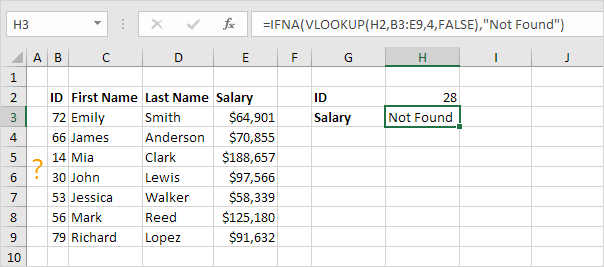
2. Use the IFNA function to convert the #N/A error into a message that is simple for users to understand.
#NUM!
When a formula has invalid numbers, Excel gives the #NUM! error message.
1. The SQRT function only works with positive numbers and cannot find square roots of negative numbers.
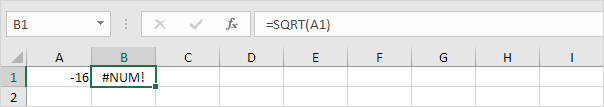
2. Enter any positive number in cell A1 and check.
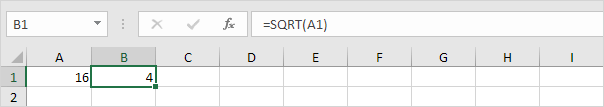
#NULL!
The intersect operator (single space) gives the values that are in both ranges. If two ranges do not intersect each other, Excel will display the #NULL! Error.
1. The formula below returns #NULL! Because the two ranges don’t intersect.
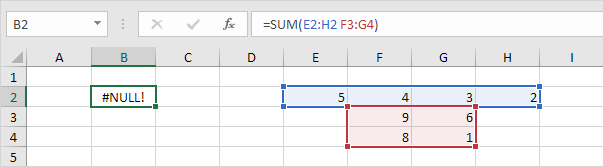
2. This formula does not give a #NULL error.
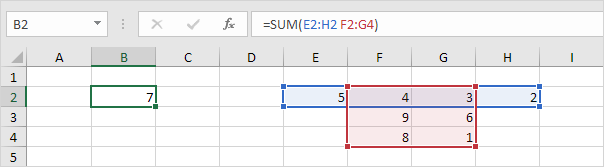
Note: =SUM(F2:G2) produces the exact same result!
#SPILL!
The #SPILL! error in Excel happens when the space for the result is blocked.
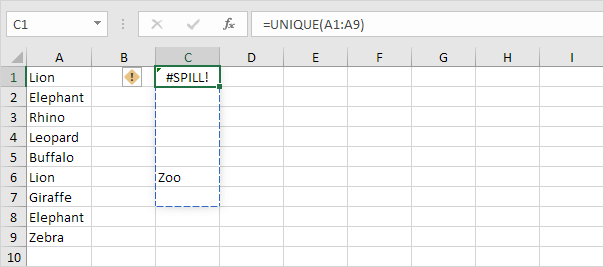
1. Make cell C6 blank to solve the #SPILL error.
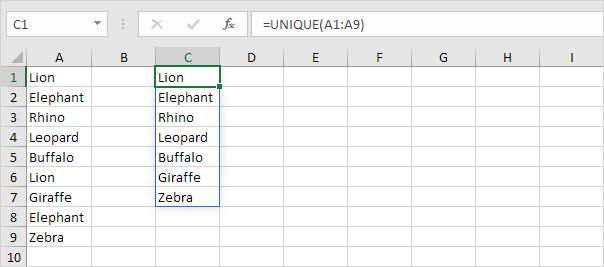
Note: By entering this dynamic array function in cell C1, multiple cells are filled automatically. Wow! Excel 365 and 2021 refer to this feature as spilling.
1/9 Completed! know formula errors in details➝
Next Chapter: Array Formulas
Leave a Reply