Logical Functions in Excel
Discover how to use the ( AND, OR, NOT, and IF ) logical functions in Excel to perform logical tests and make decisions.
Excel if Function
One of the most popular functions in Excel is the IF function and mainly used to perform logical tests. When the condition is true, it produces one result. When the condition is false, then returns another result.
1. Select cell C2, and the formula bar showsexcel logic formula a basic example of the IF function.
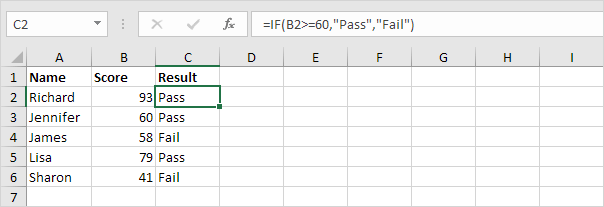
Explanation: The function returns “pass” only when the score is greater than or equal to 60. If the score is less than 60, it shows “Fail.” You can explore more examples on our IF function page.
AND Function in Excel
The AND function produces true output only when all the conditions are satisfied otherwise, it returns FALSE when any of the conditions is false.
1. Cell D2 contains a simple example that demonstrates how the AND function works in Excel.
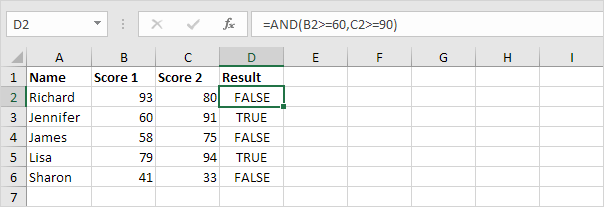
Explanation: The AND function checks if Score1 and Score2 are greater than or equal to 60 and 90, respectively. IF found true, then it returns TRUE. In any other case, it returns FALSE. Please visit our page about the AND function to learn more about how this Excel function works.
OR
The OR operator returns FALSE when all conditions are not met. For this operator to return TRUE, any of the conditions must be true.
1. Cell D2 illustrates how to apply the OR function in a basic Excel example.

Explanation: As per the condition, if any score is greater than or equal to 60, then the OR function returns TRUE. If every score is below 60, then it produces FALSE. Please visit our page about the OR function to learn more about how this Excel function works.
NOT
The NOT function reverses the value. In other words, if the input is TRUE, then it produces the output as FALSE, and when the input is FALSE, then it converts to TRUE.
1. Cell D2 shows how to use the NOT function with a basic example in Excel.
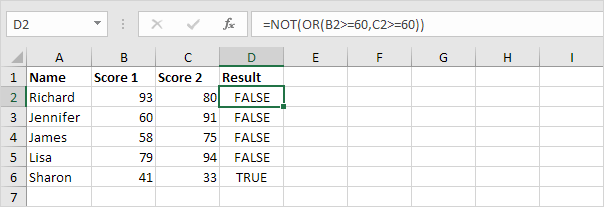
Explanation: This example shows how the NOT function turns the result of the OR function into the opposite value (see previous example).
1/11 Completed! Learn more about logical functions ➝
Next Chapter: Cell References in Excel